skip to main |
skip to sidebar
The transfer of Thermal Energy as heat requires a difference in temperature between 2 points of transfer.
Heat may be transferred by means of Conduction, Convection or Radiation.
Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy due to collisions between the molecules in the objects. Collisions between atoms and molecules trasnfer kinetic energy from the warmer to the cooler object. The object must be in Physical contact.
Convection is the thermal energy transferred by the flow of matter.
Radiation is the transfer of energy by electromagnetic radiation. Radiation can be travelled in a vacuum.

List the three ways of heat transfer and explain how it processes in the above diagram.
Conduction. The heat produced from the fire heats up the base of the pot. As the base warms up, the atoms and molecules at the base of the pot will starts to vibrate violently, and will then collide with the neighbouring atoms, causing them to vibrate as well. Thus, heat will then slowly transfer to the cooler region of the pot. However, the handle of the pot is an insulator of heat, thus heat cannot be transferred easily, hence insulators of heat are good materials to protect our hands from burns or scalding.
Convection. The fire from its source will slowly heat up the water in the pot. As the water heats up, water will expands. The density of water will then decrease and it will rise, due to the inbalance of density in water. The cool water will then sinks and as it sinks, it will get heats up again, causing it to rise. Thus a convection cycle will then goes on in the water.
Radiation. The heat produced from the fire source is give out to the surroundings. Heat is transfer to the surroundings by infra waves.
Good Conductors of Heat
Metals are good conductors of heat, as heat transfer by the movement of free electrons from hot end to cold end.
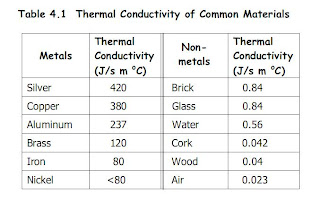
Thus, Metals are use for thermal energy to be transferred quickly through a substance.

Kettles are usually made of aluminium or stainless steel in order for fast transfer of heat to be produced. Conductors of heat absorb heat faster and thus, heat will be transfer to water to boil.

Electric Iron uses electricity to produce heat. It is used to remove wrinkles of clothings by smoothing with heat. The Ironing plate is made of Iron as Iron is a conductor of heat and thus, it will not lose heat easily and heat can be trasfer to the clothes easily and quickily.
Insulators of Heat
Isulators of heat reduces the rate of transfer of thermal energy.
Examples of Insulator of heat:
Wood, plastic, rubber, liquid, gases, glass, vacuum (perfect insulator)

Just as the Ironing plate is used as a conductor of heat, the handle of the Iron is made of plastic. Plastic is an insulator of Heat and thus, heat will not be transfer to the handle as plastic does not absorb heat. Using insulators of heat as handles serve as a protective way to prevent burns from holding Iron.


Styrofoam boxes and cups are often used to keep food and drinks warm. It is an insulator of heat and thus is does not absorb heat very much and does not transfer heat very fast. Styrofoam traps large amount of air which helps to be insulators of heat. Thus, styrofoam are good materials to prevent heat lost.
Radiation is the method of heat transfer that does not require a material medium.
It is the transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic radiation

Transfer of heat from Sun to Earth through Radiation, which takes place in a vacuum.
The Sun transfer heat to the Earth by radiation. Heat is transferred by electromagnetic waves called infra red waves. Heat transferred by infared waves are called radient heat. Conduction and convection is not possible here because of the vacuum between Sun and Earth.
Absorption and Emission of Radiation
Infared radiation is absorb and emitted by all objects and surfaces and absorbing radiant heat will result in a rise in temperature, while emitting it will result in a drop in temperature. How Hot a surface becomes depends mainly upon the amount of infrared radiation is absorbed by the surface.

If we stand near an open fire, example a fireplace or campfire, we will notice that the side of us that is facing the fire becomes much warmer than the other side overtime, even when there is no wind blowing. The hotter the object is, the more energy it radiates.
The rate of heat transfer by radiation from a hot body is affected by:
The colour and texture of the surface of a body
The surface temperature of the body
The surface area of the body
Colour and Texture of the surface of a body
A dull black surface is a better radiator of heat than a shiny surface.

Refer to the picture above, the block that is Lampblack-coated absorbed 0.97E compared to the Silver-coated block, which had only absorbed 0.10E.Hence, the darker the object is, the more radiation it will absorb.
However from the same picture as used above, we can also see that no matter which factors are affecting the amount of radiation transferred, the amount emitted and absorbed are the same.
Hence we can say that,
A rough dull black surface is both a good emitter and a good absorber.
A smotth polished surface is both a poor emitter and a poor absorber.
Surface Temperature

An object with a higher temperature will radiate heat faster. At a room temperature, a cup of water at 80 degrees (C) will radiat heat faster to the surroundings than another cup at 40 degrees(C)
Therefore,
The rate of radiation increases as the temperature increases.
Surface area

Large surface area will mean that more space will absorb heat, which will also emit the same amount of radiation. Hence, the rate of radiation increases as the surface area increases.
 We can fry an egg within minutes on a pan placed in contact with a hot plate. The heat travels from the hot plate to the pan and then to the egg by Conduction.
We can fry an egg within minutes on a pan placed in contact with a hot plate. The heat travels from the hot plate to the pan and then to the egg by Conduction.
Conduction is the main mode of heat transfer in solids.
In conduction, heat is transferred from one atom to another by the vibration of atoms.

In the diagram,
When the fixed end of the device is being heated,
point A comes into contact with point B, causing the Bell to ring
Thermal energy is transferred from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature. The heat energy flows through the strip without any flow of the material itself. Such a transfer of thermal energy without any movement of the material medium is called conduction.
The tiny particals in solids called atoms and molecules. Hence when the fix end is heated, the particales vibrate violently at the fix end. These particales will then collide with their neighbouring particles making them vibrate as well. Thus, the kinetic energy of the vibrating particales is transferred from the fix end to the rest of the strip.
Hence, Molecules moves further apart as thermal energy makes them move more quickly
Objects expand as heat is obtained.
The strip is made up of 2 different metals. When it is heated, Y will bend further than X, in order for current to flow. Thus, Y is better conductor of heat as it has a faster rate of expansion.
However, if we want to make the bimetallic strip more sensitive to temperature rise, we can coil the strips into a long spiral.
Therefore,
Conduction is the process of thermal energy transfer without any flow of the material medium
 When we place our hands over a hot stove, we can feel the heat. We are the feeling the transfer of heat. This means that thermal energy is transferred only when there is a difference in temperature.
When we place our hands over a hot stove, we can feel the heat. We are the feeling the transfer of heat. This means that thermal energy is transferred only when there is a difference in temperature.
Therefore, Thermal energy or heat is the form of energy that is transferred from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature.
Thermal energy can flow from one place to another in three ways:
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
Understand that Thermal energy is transferred from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature.
Describe how energy tranfers occurs in solids
Describe convection in fluids in terms of density changes
Explain that energy transder of a body by radiation does not require a material medium
Explain that rate of energy transfer is affected by
1) Colour & texture of the surface
2) Surface temperature
3) Surface area
Apply concept of thermal energy to everyday application
Class 3A2 Pure physics Chapter 10 Thermal Energy NoesReg. 4. Tadas~

























